Building a start-up on emerging technologies can be a challenge as there are pitfalls to recover from and the risk factors that haunt the start-up progression. With the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT), the adoption of autonomous systems like smart grids, autonomous automobile systems, medical monitoring has become more prominent and widespread.
IoT-based applications have seen much developmental significance for new start-ups. The start-up ecosystem has seen the technological advantage of applications-based business models and with connected networks of IoT devices, the whole scenario has seen rapid changes and adoption of several methods to optimize the application development to minimize the cost of development.

So, where does the MVP(Minimum Viable Product) method fit in? For this answer, we need to understand some facts about start-ups! When we talk about start-ups, 42% start-ups fail due to a lack of products or services that the market needs and in 2018, 4228 start-ups exit were recorded worldwide. Thus, when it comes to the vital question of start-up success based on its market and product, the Minimum Viable Product(MVP) method becomes an absolute necessity.
What is the Minimum Viable Product(MVP)?
Start-ups are more of experimentation in the problem-solution domain and which often end up with launching a product that greatly differs from the original idea. Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a representative proxy of the final product that is used to validate either new technology or to elicit customer requirements. It is a core concept of lean anufacturing/production that is used in start-up product development for new technologies.

MVP can be anything such as, a short animation that explains what your product does and why users should buy it or it can be a user interface that looks like a real working product but the actual business process is manually carried on. This method saves money and time through effective simulation of product and its actual working while yet in the pre-production phase, to enable the realization of product pitfalls to be overcome before the production and deployment.
Types of MVP that can be used for IoT Apps Development:
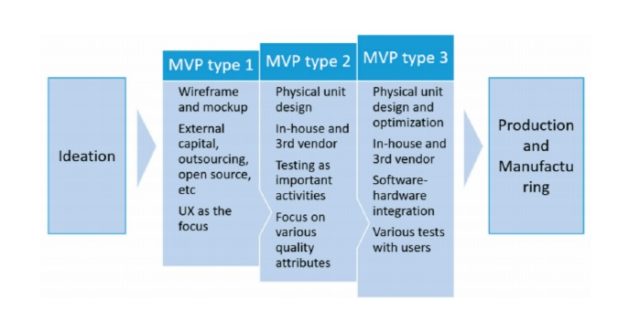
1. UX Focused MVP:
This MVP is focused on the user experiences and it simulates the interaction of a user and the system with ease. The actual functionalities of the MVP are manually carried on with the internal development effort limited due to a lack of available funding. It utilizes tools like rapid prototyping, local contractors/vendors and ready-made components.
Key Components:
- Setup of the wireframe of the application.
- Finding external funding, hiring offshore developers or open-source vendors.
- Focusing the complete process on user experience.
2. Quality Based MVP:
The evolution of the second type is a progression of UX focused MVP with its initiation from ideation and a forward progression towards the production and development of IoT apps. This type of MVP involves hardware unit design, including sensor integration with chips, circuit design, and system engineering to align the physical IoT units with the interfaces or APIs of the IoT applications.
The product development is completely focused on all possible functionalities. Final qualities of the final product are considered prime metrics and most of the designing is done in0house with few testing and other activities assigned to outsourced contractors and vendors.
Key Components:
- Complete designing of the apps and IoT.
- In-house and third-party vendors for the integration of quality attributes.
- Testing the vital functionalities based on APIs interaction with IoT physical devices.
3. Testing Based MVP:
Testing type MVP shifts the focus from physical IoT devices to the development of applications for IoT devices. Focus on product validation is realized through data visualizations and processing the components of the product. This type integrates all the earlier types to design and optimize them for the best quality applications.
Acceptable lot of MVPs are selected for the further process of rapid prototyping with a standard of Minimum Acceptable Quality. The integration of physical IoT devices and IoT applications is done seamlessly and the testing of the complete product is done regressively.
Key Components:
- Complete integration of hardware and software components.
- Complete design optimization
- Focused on the testing of IoT apps for its physical devices.
Benefits of MVP for IoT apps:
- It makes life easier for start-ups that build their products from scratch and the complexity of design is much more daunting.
- It helps calibration and testing of architectural decisions that depend on the selected components for central processing technologies, sensors and IoT nodes.
- It increases the efficiency and reduces the cost of manufacturing of IoT components.
- It helps Start-ups to use open-source components for the degree of openness and the level of support available from the open-source community.
- It helps the effective integration of application APIs and IoT physical devices APIs.
- MVP helps effective testing of the IoT applications and provide valuable feedback for changes.
Wrapping it Up:
IoT has outgrown many other emerging technologies in terms of investments, trends, and popularity. In 2019, the total mobile revenue saw 2.2% of IoT application revenue contribution which is expected to improve by 3% to rise to 5.2% by 2025.
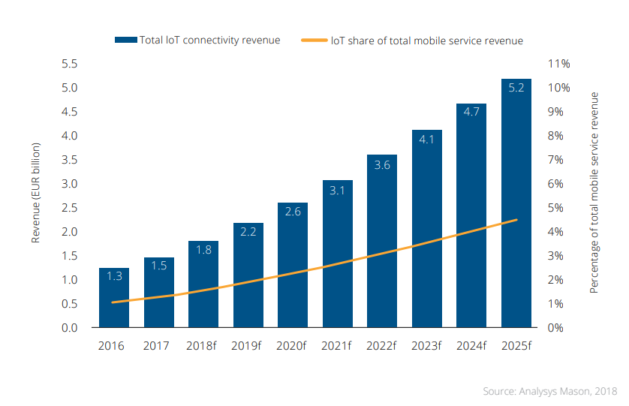
This data suggest the soaring market of IoT apps for mobile revenues and this is bound to encourage new start-ups and entrepreneurs to look upon more interesting ways to develop IoT apps for their businesses. Hence, with MVP the risk minimization of product development can be achieved and worth of the product can be realized before the grand launch!





Leave a comment